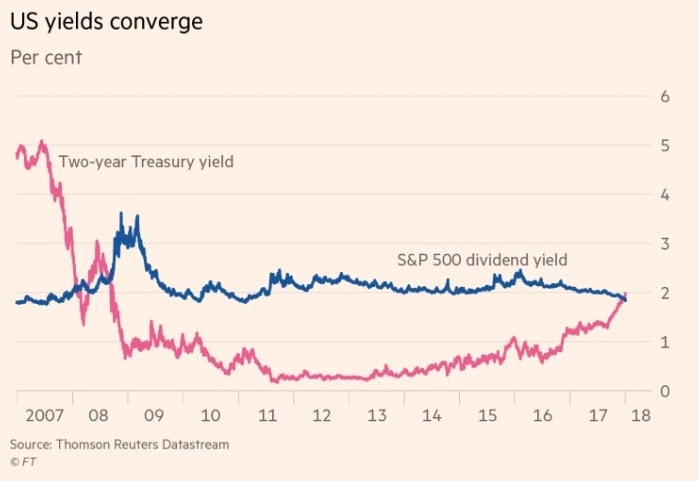
Dividend Yields Compared to Bond Yields (S&P 500)
The dividend yield is the return a company gives to its shareholders, and it is measured as a percentage of the share price. The average dividend yield of the S&P 500 companies can be an indicator for the relation of the price of a stock compared to the dividend the shareholder receives.
Especially a comparison with the U.S. treasury bonds might make sense, as investors will be more and more tempted to invest in bonds instead of stocks when the treasury rates and the dividends are similar, as the risk for bonds is lower. However, you also have to keep the share price and the bond price itself in mind. When making this decision, as for bonds and stocks, the return can be made on regular payments (interest rates for bonds, dividends for stocks) and market price on a secondary market (market price of bond or stock).
Key takeaways:
- The dividend yield is the percentage of the stock price that is paid as a dividend to the investor.
- the lower it is, the more expensive stocks are
- the closer the percentage is to treasury bonds, the more investors are tempted to invest in bonds, and the stock market may go down